
AI and Biometric Data: Injury Prediction
AI is changing how injuries are predicted in sports. By analyzing real-time biometric data from wearables, GPS trackers, and historical injury records, AI models can flag athletes at risk of injury before it happens. This has major implications for both team performance and sports betting.
Key Takeaways:
- How it works: AI uses data like heart rate variability, sleep quality, movement patterns, and workload to produce daily injury risk scores for players.
- Impact on betting: Injuries to key players can quickly shift betting odds. AI tools like Digital Athlete and WagerProof help bettors act on injury predictions before sportsbooks adjust.
- Accuracy: Algorithms like Random Forest and deep learning models have achieved up to 90.5% accuracy in predicting injuries.
- Types of data used: Physiological metrics, biomechanical data, workload indicators, recovery stats, and past injuries are key inputs for AI systems.
AI injury prediction tools are giving bettors and teams a competitive edge by offering early warnings, improving decision-making, and reducing financial losses tied to unexpected injuries.
NFL uses AI to predict player injuries - here’s how it could help the Bears
Types of Biometric Data Used in AI Injury Prediction
AI injury prediction relies on five key biometric categories to assess and predict potential risks.
- Physiological metrics include indicators like rMSSD, resting heart rate, SmO2, and core temperature, offering a snapshot of an athlete's baseline health.
- Biomechanical data tracks gait and neuromuscular patterns through tools like accelerometers and gyroscopes.
- Workload indicators measure factors such as the Acute:Chronic Workload Ratio (ACWR), cumulative minutes played, training intensity, and "Player Load", a metric derived from wearable devices.
- Recovery and wellness data focus on sleep quality, respiratory patterns, and subjective wellness ratings to gauge readiness.
- Historical injury records complement live data, creating a more comprehensive risk profile.
For instance, a drop in heart rate variability (HRV) exceeding 20% compared to an athlete's morning baseline may indicate parasympathetic fatigue, increasing injury risk. Similarly, an ACWR above 1.5 highlights musculoskeletal overload, while gait asymmetry deviations of over 10% suggest biomechanical instability.
These metrics, when combined, set the foundation for advanced wearable tracking and the integration of historical data to refine injury predictions.
Wearable Sensors and Tracking Devices
Wearable sensors are at the heart of real-time data collection, providing insights that can lead to immediate interventions. GPS trackers, such as Catapult systems operating at 10 Hz, capture velocity, acceleration, and distance. During the 2020–2021 season, a Portuguese first-division football team used Catapult GPS receivers to predict non-contact injuries. The system, paired with Support Vector Machines, achieved a sensitivity of 71.43% and an overall accuracy of 74.22%.
Other tools include heart rate monitors and wearable ECG devices for HRV measurements, near-infrared spectroscopy sensors for muscle oxygenation, electromyography sensors for muscle activity, and smart mouthguards that capture impact data. Force plates, meanwhile, assess power output and acceleration, helping to identify biomechanical weaknesses.
Combining Past Injury Records with Live Data
Historical injury data significantly enhances the predictive capabilities of AI. By integrating past injuries with real-time metrics, individualized risk models are created. For example, a study published in December 2025 tracked 300 male professional football players from a Tier-1 team in Guangzhou, China, during the 2021–2022 seasons. Using a Random Forest model that combined historical injury records with HRV (rMSSD) and training workload data, researchers achieved an impressive 90.5% AUC. SHAP values in the study confirmed prior injury as a leading predictor.
"Previous injury was a meaningful indicator of future injury, which has been demonstrated in multiple sports with different injury types." - Journal of Sports Analytics
Between 2010 and 2020, the METIC model analyzed data from 856 NBA players, covering 11,000 injuries. By incorporating sequences of past injuries alongside game-specific statistics, this deep learning approach doubled the F1 score of the next best model. This combination of live and historical data enables AI to detect subtle changes in movement quality, which might only become meaningful when compared to a player's injury history. This capability underscores the growing importance of injury prediction, not just for player safety but also for strategic decisions in sports betting.
Machine Learning Methods for Injury Prediction
AI Injury Prediction Accuracy Across Sports and Algorithms
AI Algorithms Used for Injury Forecasting
Tree-based ensemble methods are particularly effective for handling the complex, non-linear nature of sports data. Algorithms like Random Forest and XGBoost can analyze multiple factors simultaneously - such as training intensity, recovery stats, and biomechanical patterns - without assuming straightforward relationships between variables.
For example, a study conducted in Guangzhou, China, between 2021 and 2022 tracked 300 male professional football players using a Random Forest model with 500 trees. The model delivered an impressive 85.6% accuracy and a 90.5% AUC, showcasing its ability to process intricate variable interactions. Similarly, XGBoost variants have shown strong performance, achieving 84% precision in predicting injuries among elite youth athletes.
Deep learning models are also gaining traction for injury risk prediction. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) excel at analyzing video footage and sensor data to detect unusual movement patterns, while Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are adept at monitoring fatigue over time, flagging dangerous workloads before injuries occur.
A standout example is the METIC model, which uses transformer-based architecture to analyze a decade of NBA data (2010–2020). By processing sequences of past injuries and game stats, METIC achieved a 0.80 ROC AUC, demonstrating its capability in identifying patterns tied to injury risks. On smaller datasets, Support Vector Machines (SVMs) have also proven effective, distinguishing between high-risk and low-risk athletes based on training and recovery data.
These advanced algorithms offer valuable insights for assessing injury risks across different sports.
Prediction Accuracy Rates Across Sports
The effectiveness of these algorithms varies depending on the sport and specific prediction scenarios. Whether for teams or bettors, these models are shaping how injury risks are evaluated, influencing both player management and betting strategies.
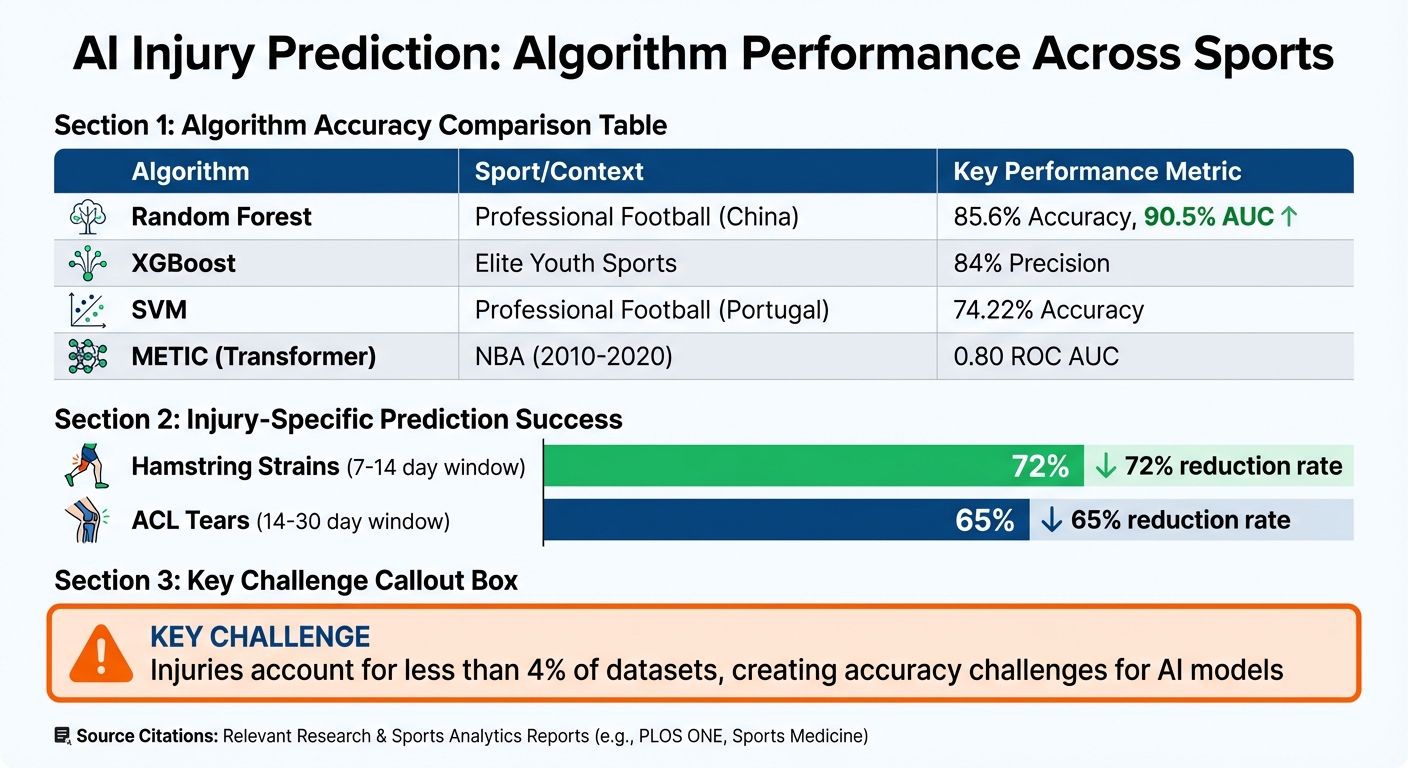
| Algorithm | Sport/Context | Key Performance Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | Professional Football (China) | 85.6% Accuracy, 90.5% AUC |
| XGBoost | Elite Youth Sports | 84% Precision |
| SVM | Professional Football (Portugal) | 74.22% Accuracy |
| METIC (Transformer) | NBA (2010-2020) | 0.80 ROC AUC |
The accuracy of these models also hinges on factors like the type of injury and the prediction window. For instance, models targeting hamstring strains within a 7-14 day window have achieved 72% reduction rates, while predictions for ACL tears within a 14-30 day window have reached 65% reduction rates. However, a major challenge remains: injuries are rare, often accounting for less than 4% of datasets. This rarity can skew results, as models may achieve seemingly high accuracy by simply predicting "no injury" across the board.
"The discrepancy among METIC feature importance and relative risk factors highlight the non-linear complex relationship among athlete data points and injuries." - Journal of Sports Analytics
To tackle these challenges, explainable AI tools like SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) are now being used to give coaches deeper insights. These tools help pinpoint why a model flags an athlete as high-risk, often identifying key factors like sudden increases in high-speed distance or significant drops in recovery metrics.
How Injury Predictions Change Betting Decisions
Anticipating Line Movements from Injury Data
AI-driven injury predictions are reshaping how bettors make decisions, especially when it comes to reacting before the market adjusts. These forecasts provide a key advantage: the ability to act quickly based on early warning signs. For example, when AI detects that a player might be at risk - using data like heart rate variability, training load, or subtle movement patterns - savvy bettors can place their wagers before sportsbooks catch on and adjust the odds.
Take Digital Athlete, which sends alerts up to 48 hours in advance, giving bettors enough time to capitalize on odds that still assume a star player is in peak condition. Once the market starts factoring in the injury risk - whether through rumors or an official "questionable" status - the lines shift, often erasing any potential edge. Acting early is key.
AI also updates win probabilities in real time as biometric data changes, which directly impacts betting odds. Christian Chase from Vanderbilt Law School explains it best:
"Imagine having the ability to look at the heart rate of a Quarterback who is about to attempt a two-minute drill with the game on the line: It spikes? Bet his team loses. It doesn't? Bet the house on him".
Traditional injury reports may miss subtle but important red flags. AI, on the other hand, identifies patterns - like non-linear outliers - that suggest elevated risks for muscle strain. Since the release of Digital Athlete's platform in 2023, the NFL has seen a 14% decrease in practice-related lower-extremity strains. This shows how effective these tools are in spotting risks before they turn into actual injuries.
This level of foresight empowers platforms like WagerProof, which deliver precise, actionable data to bettors, turning injury risk insights into data-driven betting strategies.
Accessing Biometric Insights Through WagerProof

Platforms like WagerProof bring injury prediction data directly into the hands of bettors, offering tools that explain why certain bets hold value based on injury forecasts. The platform's real-time sports data system is built to surface exactly the kind of insights that give bettors an edge.
WagerProof’s automated outlier detection system identifies mismatches in the market - like when injury risks aren't fully priced into the odds. With instant alerts, bettors can anticipate line movements and act before sportsbooks adjust, giving them the same edge that professional bettors rely on. On average, this approach helps beat closing lines by 3-7% across various sports.
Another standout feature is WagerBot Chat, which provides real-time answers to specific questions about a player’s workload, fatigue levels, or injury risks. Unlike generic AI chatbots, WagerBot relies on actual biometric data, ensuring accurate and actionable insights. It combines prediction markets, historical stats, public betting trends, and statistical models into a single interface, making it easier to verify injury predictions against current market odds.
The platform also includes an Edge Finder, which pinpoints value bets by comparing AI-generated injury probabilities with sportsbook odds. For example, if a sportsbook hasn’t adjusted for a player’s elevated injury risk - perhaps because the biometric data isn’t public yet - WagerProof sends a fade alert. This proactive system turns raw data into actionable advice, helping bettors make informed decisions before the market catches up.
Conclusion: AI and Biometric Data in Sports Betting
AI-driven biometric analysis is reshaping sports betting by predicting player injuries up to 48 hours in advance. Tools like the NFL’s "Digital Athlete" and the NBA’s real-time optical tracking systems analyze data from wearables, movement patterns, and historical injury records. This allows bettors to act on injury forecasts before sportsbooks adjust their lines, offering a critical edge.
This shift from reactive injury updates to proactive forecasting is a game-changer. With about one-third of professional football injuries linked to overuse and often predictable, access to this data creates a significant advantage. Bettors can leverage the same type of insights teams use to manage player health, but for betting strategies.
Transparency is just as important as accuracy. Derek McHugh from Kitman Labs highlights this perfectly:
"If a coach can't easily understand why the algorithm has arrived at its injury prediction, they can't begin to take action to mitigate an athlete's elevated risk".
The same applies to bettors. Understanding why a risk exists - like shifts in key performance metrics - adds far more value than simply seeing a prediction.
Platforms like WagerProof take this concept to the next level. Using automated outlier detection, real-time data integration, and explainable AI tools like WagerBot Chat, WagerProof alerts bettors when injury risks aren’t fully priced into the odds. By turning raw data into actionable insights, it helps bettors make smarter decisions before sportsbooks adjust.
The future of sports betting lies in decoding biometric signals to predict injuries. Platforms that combine real-time accuracy with transparency will empower bettors to make more informed and strategic wagers.
FAQs
How does AI predict sports injuries using biometric data?
AI has become a game-changer in sports by analyzing biometric data from athletes to predict injuries. This data comes from wearable devices like GPS trackers or sensors that monitor metrics such as movement patterns, workload, and physical stress levels.
By applying advanced algorithms, AI can detect patterns that might signal an increased risk of injury. For instance, if an athlete's movement deviates from their usual patterns or if signs of overtraining appear, these could be red flags. With early warnings from these models, teams can take proactive measures to reduce injury risks, enhance performance, and make smarter decisions using real-time insights.
How do AI injury predictions influence sports betting strategies?
AI-driven injury predictions are transforming sports betting strategies by providing detailed insights into player health and availability. These models process biometric data to predict injury risks, allowing bettors to anticipate lineup changes or shifts in player performance.
Armed with this knowledge, bettors can spot opportunities for better odds, tweak their wagers based on injury probabilities, and make more informed decisions. Staying ahead of these predictions can give you an advantage in forecasting game outcomes and identifying discrepancies in odds.
How do wearable sensors help predict and prevent injuries?
Wearable sensors are transforming how injuries are predicted and prevented in sports. These devices continuously track an athlete's biomechanical and physiological data, offering a detailed look at metrics like joint movement, muscle activity, and gait patterns. By monitoring these aspects in real-time, they can detect unusual movement or excessive strain - key indicators of potential injuries.
AI takes this a step further by analyzing the collected data to forecast injury risks. It combines factors like historical performance, game activity, and individual biomechanics to deliver more precise predictions. This forward-thinking approach enables timely interventions, keeping athletes healthier and helping them maintain peak performance.
Related Blog Posts
Ready to bet smarter?
WagerProof uses real data and advanced analytics to help you make informed betting decisions. Get access to professional-grade predictions for NFL, College Football, and more.
Get Started Free