Machine Learning vs. Time Series in Betting
Which is better for betting: machine learning or time series analysis? It depends on the situation. Machine learning models are great for analyzing complex pre-game data, like player stats, weather, and injuries. Time series analysis, however, is better for live betting because it tracks patterns like momentum and trends during games.
Key findings:
- Machine learning shines in pre-game analysis, handling diverse data and spotting non-linear patterns.
- Time series excels in live betting, focusing on sequential data like momentum shifts and streaks.
- Calibration (aligning predictions with real-world outcomes) matters more than accuracy for profitability.
- A hybrid approach combining both methods often works best for maximizing betting success. For more sports betting insights, explore our latest guides.
Quick Comparison
| Criteria | Machine Learning | Time Series Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Pre-game betting | Live betting |
| Strengths | Handles diverse data, non-linear patterns | Tracks trends, momentum, and time-dependent data |
| Weaknesses | Needs large datasets, risks overfitting | Struggles with random events, limited to sequential data |
| Profitability Focus | Calibration over accuracy | Works well when patterns are stable |
The article dives deeper into these methods, their strengths, limitations, and how combining them can improve betting outcomes.
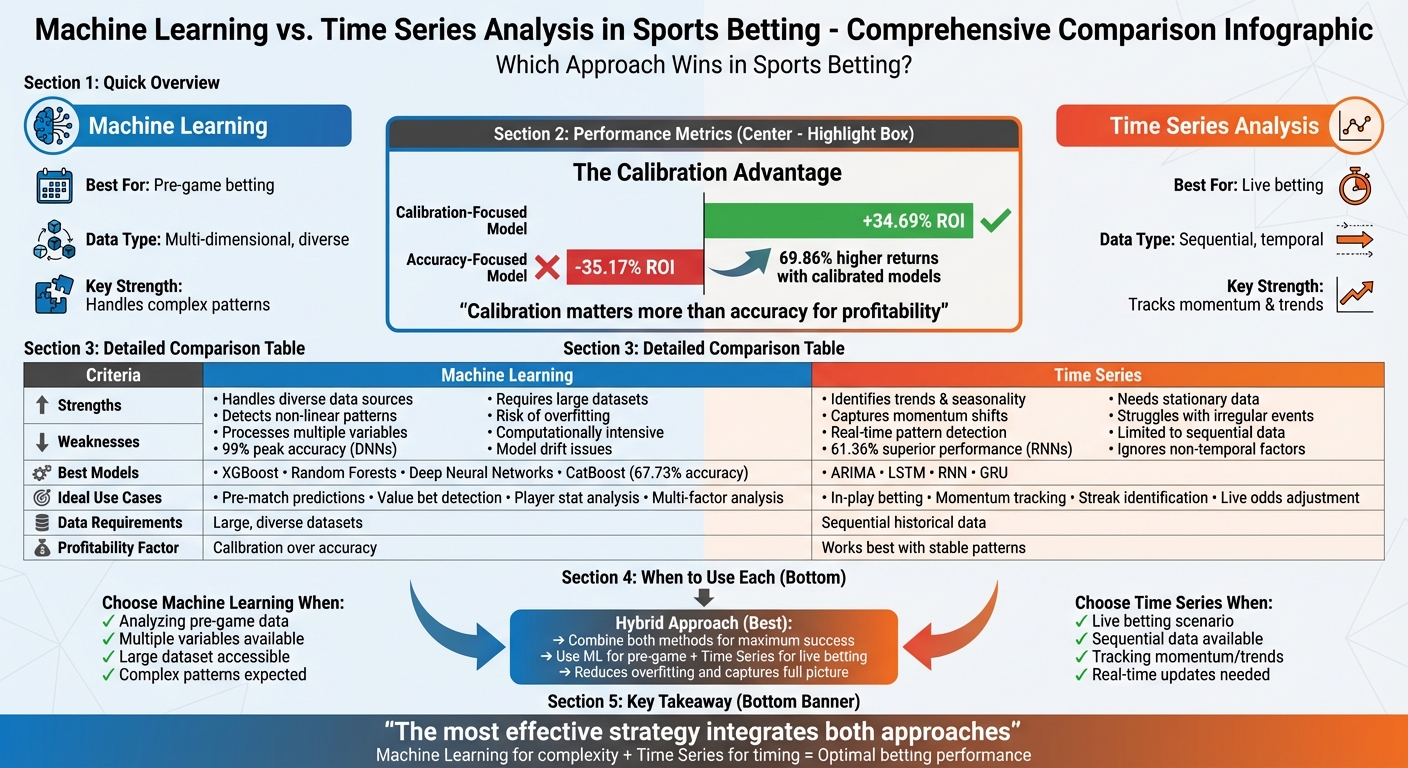
Machine Learning vs Time Series Analysis for Sports Betting: Complete Comparison
Introduction to machine learning for sports betting
Machine Learning: Strengths and Applications
Machine learning models shine when it comes to unraveling complex, multi-dimensional sports data. Unlike traditional models that rely on linear assumptions, algorithms like Random Forests, XGBoost, and neural networks can detect intricate relationships across diverse variables. This makes them incredibly useful for combining player stats, team performance metrics, weather conditions, and even injury reports into a cohesive prediction.
Processing Complex Features
One of the standout abilities of machine learning is its knack for turning detailed data into practical insights. Take Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), for example. These models can analyze matrices of player statistics and automatically determine which combinations matter most for predicting team outcomes. Between 2007 and 2014, researchers Ondřej Hubáček, Gustav Šourek, and Filip Železný developed an NBA betting system using CNNs. Their system transformed individual player-level stats into team-level features, enabling them to consistently generate profits by spotting inefficiencies that simpler models missed.
This approach goes far beyond basic averages. Machine learning models can calculate "relative out-performance values", which measure how teams perform compared to previous opponents. This highlights momentum and form - factors that static stats often fail to capture. Such advanced feature engineering naturally leads to selecting the best model architecture for precise predictions.
Model Types and Performance
Different machine learning models excel at solving specific prediction challenges. XGBoost and Random Forests are particularly effective for general outcome predictions in sports like soccer and basketball, as they can handle non-linear patterns without overfitting. Meanwhile, Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) can deliver exceptional accuracy when fed large datasets. For instance, researchers Deng and Zhong analyzed European soccer data from 2008 to 2016, achieving an impressive 99% peak prediction accuracy across 11 countries.
But accuracy alone doesn’t guarantee profitability. A Random Forest model designed to estimate player market valuations achieved an R² value of 0.948, outperforming linear regression. The real game-changer, however, was calibration. Researchers from the University of Bath showed that a well-calibrated model capable of estimating probabilities accurately could achieve a +34.69% ROI, while an accuracy-focused model might lose 35.17%. The key difference? Calibration ensures the model’s predicted probabilities align closely with real-world outcome frequencies - a crucial factor for betting strategies like the Kelly Criterion.
"Machine learning models... can uncover intricate relationships and trends that may not be apparent to human analysts." - René Manassé Galekwa, Researcher
These strengths, as impressive as they are, come with their own set of challenges, which we’ll delve into next.
Machine Learning: Weaknesses and Limitations
Even though machine learning models are powerful, they come with certain weaknesses that can limit their reliability, especially in dynamic sports settings. Being aware of these shortcomings is key to creating predictive systems that consistently deliver accurate results.
Overfitting and Data Requirements
One major issue with machine learning models is overfitting - when models latch onto historical patterns that may no longer apply. In sports, where team rosters, coaching strategies, and playing styles are constantly changing, relying on static stats like total blocks per game can be misleading. Moreover, standard random cross-validation can inadvertently mix future events into training data, which undermines predictive accuracy. Research shows that models emphasizing calibrated probabilities often outperform those focused solely on picking winners, as they better estimate the likelihood of outcomes.
"A highly accurate predictive model is useless as long as it coincides with the bookmaker's model." – Hubáček et al.
Another limitation is the dependence on large, high-quality datasets. For example, some researchers skip the first 10 games of an NBA season because early-season data lacks statistical depth. In sports with limited historical data or incomplete records, this reliance becomes a significant barrier. Beyond data quality, the way machine learning models handle individual events as isolated instances creates additional challenges, as discussed below.
Challenges with Time-Dependent Patterns
Capturing the sequential nature of sports is another area where machine learning models fall short. These models often treat every data point as independent, ignoring factors like player fatigue, team momentum, or shifting game dynamics. Unlike time series analysis - which breaks data into trends, seasonality, and random variations - traditional machine learning models struggle to account for these patterns.
For instance, a study by Sascha Wilkens in September 2021 on professional tennis (ATP and WTA) highlighted that even with detailed player and match data, prediction accuracy rarely exceeded 70%. This is largely because most of the critical information was already embedded in betting market odds. While advanced architectures like RNNs or LSTMs can analyze sequential patterns, they are computationally demanding and require significant resources to implement. Without such specialized designs, machine learning models may fail to distinguish meaningful trends from noise, which can greatly reduce their effectiveness in sports betting, where timing often reveals crucial insights.
Time Series Analysis: Strengths and Applications
Unlike typical machine learning models that treat each game as a standalone event, time series analysis focuses on how patterns develop over time. This approach is particularly good at breaking data into components like trends, seasonality, and random fluctuations. By digging into these elements, bettors can uncover momentum changes, streaks, and performance rhythms that might slip past conventional models.
Identifying Trends and Seasonality
Models such as ARIMA and LSTM are specifically crafted to identify evolving patterns across games. ARIMA, a statistical model, shines when working with data that’s relatively stable and predictable. On the other hand, deep learning models like LSTM are better suited for handling fluctuating, long-term data.
"Statistical models perform best for datasets with low stochasticity, deep learning models specialize in forecasting fluctuant and long-term time series data." – Ang Xuan, Mengmeng Yin, Yupei Li, Xiyu Chen, Zhenliang Ma
RNNs, including LSTM models, are particularly adept at capturing long-term dependencies, with research showing strong performance in 61.36% of cases. This ability to retain memory makes them highly effective for identifying winning streaks, performance slumps, or seasonal trends. For instance, they can detect shifts during back-to-back games or playoff stretches. These strengths also make time series analysis a valuable tool in live betting, where conditions evolve rapidly.
Live Betting Applications
Time series analysis truly shines in live betting, where odds need constant adjustment as the game progresses. Unlike pre-match predictions that rely on static data, live betting involves processing a continuous stream of information - tracking momentum shifts, scoring runs, and key game events. These models excel at handling sequential uncertainty, which is critical for making real-time odds adjustments.
"The entire live betting experience depends on the speed and accuracy of the data feed." – Insurance-Edge
Additionally, time series–based anomaly detectors can spot unusual betting patterns, highlighting opportunities before odds catch up. For bettors, this means these models can exploit market inefficiencies, giving them an edge in fast-paced betting environments where conditions change in the blink of an eye.
Time Series Analysis: Weaknesses and Limitations
While time series analysis is great for identifying trends, it has limitations that can impact its predictive reliability. Despite its ability to track momentum and live betting scenarios, these models face challenges that make them less effective in sports betting. Much of this stems from the assumptions they make about data patterns and the type of information they prioritize.
Stationarity Requirements and Irregular Events
Time series models rely on the assumption of stationarity, meaning the data's mean, variance, and patterns stay consistent over time. However, sports data is anything but stable. Games are often unpredictable, with outcomes influenced by random events that disrupt the steady patterns these models depend on.
Unpredictable factors - like player injuries, trades, or sudden weather shifts - can throw off these models. For example, if a key player is injured or a team makes a mid-season roster change, the established patterns break down. Traditional time series models struggle to adapt to these abrupt changes, leading to spikes in unexplained variance, also known as "residue." This variance reduces the accuracy of predictions. These disruptions highlight a major limitation of time series analysis, especially when compared to more flexible and adaptive modeling approaches.
Non-Sequential Data Limitations
Time series analysis is primarily designed to work with sequential data - such as past scores, point spreads, or game-by-game performance records. While this is useful, it ignores critical non-sequential factors that often play a key role in determining outcomes. Elements like player stats, team chemistry, home-court advantage, or specific matchups aren't tied to temporal sequences and are, therefore, overlooked.
Machine learning models, on the other hand, excel in processing diverse data types, including non-sequential information. They can analyze multiple variables - regardless of their order - offering a more detailed understanding of game dynamics. For sports bettors, this distinction matters because some of the most valuable insights come from knowing who is playing and how teams stack up against each other, not just when they last played. This broader perspective makes machine learning a better fit for capturing the full complexity of sports predictions.
Machine Learning vs. Time Series: Direct Comparison
While earlier sections explained how these methods work, this section dives into their real-world impact on betting outcomes. These aren't just theoretical differences - they directly affect your bottom line.
Performance Metrics
Recent studies show that accuracy alone doesn't guarantee profitability. In March 2023, researchers Conor Walsh and Alok Joshi tested two NBA betting strategies. One relied on model calibration and achieved a +34.69% ROI, while the other, based on accuracy, resulted in a -35.17% loss. This highlights a crucial point: calibration, not accuracy, drives profits.
"Model calibration is more important than accuracy for sports betting."
– Conor Walsh and Alok Joshi, Department of Computer Science, University of Bath
You could have a model that's great at picking winners but still lose money if its probability estimates are off. For instance, if your model predicts a 60% chance of a team winning, that outcome needs to occur about 60% of the time. This level of precision is what separates successful betting strategies from guesswork.
When it comes to specific models, tree-based approaches like XGBoost and LightGBM are excellent at handling tabular data efficiently. Meanwhile, RNNs and LSTMs shine in processing sequential data, outperforming in 61.36% of cases. These stats not only show profit potential but also help in choosing the right model for your data.
Best Use Cases
The choice between machine learning and time series models often depends on the betting scenario.
- Machine learning models are best for pre-game betting. They can process a wide range of factors - like player stats, team records, matchup history, and injury reports - all at once. Tools like XGBoost are particularly effective at identifying value bets where bookmaker odds deviate from true probabilities.
- Time series models excel in live betting situations. During in-play betting, the sequence of events becomes critical. For example, LSTMs can analyze momentum shifts, scoring streaks, and the evolving flow of a game in real time. In cricket betting, LSTM networks analyzing ball-by-ball data from the Indian Premier League (IPL) have consistently outperformed traditional models, thanks to their ability to capture the time-dependent nature of the game.
In short, use machine learning for pre-game analysis and time series models for live betting scenarios. Each approach has its strengths, and knowing when to use which can make all the difference.
Selecting the Right Approach
Picking the right tool depends on your data type, betting scenario, and available computational resources. This decision lays the groundwork for choosing the best sports betting strategies for both pre-match and in-play betting.
If your data is linear and relatively noise-free, ARIMA models are a solid choice. On the other hand, machine learning methods like Random Forests excel in handling more complex, noisy datasets. Machine learning shines when analyzing multiple variables at once - think player injuries, weather, or historical stats - while time series models focus on sequential historical data to uncover patterns over time.
"Machine learning models, particularly those that incorporate real-time data, are crucial to maintaining competitive odds that attract bettors while ensuring profitability for bookmakers." – René Manassé Galekwa, Institute of Smart Systems Technologies
Computational efficiency also plays a role. While deep learning models like LSTM are great at capturing intricate temporal patterns, they require significant processing power. For quicker updates and training, simpler alternatives like Gated Recurrent Units (GRU) may be more practical.
When Machine Learning Works Best
Machine learning is particularly effective for pre-match betting, where analyzing multiple variables simultaneously is key. Its real power lies in uncovering complex interactions that traditional models might miss. For instance, in early 2024, researchers Wang et al. introduced TacticAI, a geometric deep learning tool for Liverpool FC. By analyzing 7,176 corner kicks from the 2020–2021 Premier League season, it offered tactical recommendations that expert coaches preferred 90% of the time over existing methods.
Machine learning also excels at value detection, identifying mismatches between bookmaker odds and true probabilities. For example, Deep Neural Networks (DNN) have achieved a 99% accuracy rate in soccer predictions, outperforming Decision Trees (91%) and Random Forests (84%). Models like CatBoost and XGBoost are particularly adept at handling categorical data, with CatBoost achieving up to 67.73% accuracy in predicting soccer match results. However, accuracy alone doesn’t guarantee betting success - profitability depends on more than just prediction precision.
That said, machine learning requires a large dataset to perform well. Without enough training data, models risk overfitting. This can be a challenge in sports with limited historical data or when predicting outcomes for newly formed teams, where reliable patterns are harder to establish.
When Time Series Works Best
Time series analysis is the go-to for live betting, capturing trends, seasonality, and momentum shifts as they happen. Its strength lies in modeling temporal dependencies, showing how past events influence future outcomes. This makes it especially useful for in-play betting, where understanding the flow of the game is critical.
One major advantage of time series models is their interpretability. They clearly show how trends, seasonality, and patterns affect predictions, making it easier to understand why a certain outcome is expected. These models work best with low-noise, stationary data where patterns repeat consistently - like the seasonal increase in home run rates during summer baseball games.
However, time series models have their limits. Irregular events - such as sudden player injuries or coaching changes - can disrupt predictions, as these don’t follow regular temporal patterns. In such cases, supplementing time series analysis with machine learning or switching entirely to a machine learning approach may be necessary. Recognizing these strengths and weaknesses helps ensure accurate predictions and better betting decisions.
Using Both Approaches with WagerProof

WagerProof combines machine learning with time series analysis to give bettors a well-rounded perspective on betting opportunities. The platform's consensus system integrates long-term simulations with real-time news analysis. This dual approach reduces the risk of overfitting while identifying odds that may be mispriced.
Real-Time Data and Value Detection
WagerProof’s integrated model delivers insights in real time, making it easier to spot valuable opportunities. Its Edge Finder tool compares market spreads across different models to identify inefficient odds. By blending models with varying error patterns, it achieves a balance between bias and variance, ensuring more stable predictions. When public sentiment causes market prices to deviate from actual statistical probabilities, the Edge Finder flags these discrepancies, helping users take advantage of the gaps.
The platform also uses model calibration to align predicted probabilities with real-world outcomes, ensuring long-term profitability and effective bankroll management. A model that simply mirrors bookmaker odds won’t provide an edge, regardless of its accuracy. WagerProof goes further by integrating advanced metrics like Elo ratings, Expected Goals (xG), and Player Efficiency statistics, offering a deeper and more nuanced view of potential game outcomes.
WagerBot: AI-Powered Betting Assistant
To enhance its data-driven insights, WagerProof includes an AI assistant for dynamic betting analysis. WagerBot Chat connects to live professional data, combining machine learning's ability to recognize patterns with time series analysis that tracks momentum shifts. Unlike generic AI tools, WagerBot uses live statistics to evaluate betting options as they change, addressing both pre-match scenarios (where machine learning excels in processing multiple variables) and live betting situations (where time series models detect trends and seasonal patterns).
Additionally, WagerProof provides expert picks from Real Human Editors, who confirm high-value opportunities and explain the mathematical reasoning behind their recommendations. This level of transparency sets WagerProof apart from black-box systems that offer no explanations or cappers who hedge their bets by giving different picks to different users. With these tools, data, and expert insights, WagerProof empowers users to make smarter betting decisions.
Conclusion
Machine learning and time series analysis each bring unique strengths to sports betting, and understanding when to apply them can make all the difference. Machine learning excels at processing complex datasets - like player stats, weather conditions, injury reports, and even social media sentiment. This makes it a powerful tool for setting pre-match odds and ensuring market consistency. On the other hand, time series analysis shines in live betting and micro-markets, where it captures temporal patterns and updates odds quickly in response to real-time events.
One of the keys to success in betting models is calibration. Research from June 2024 revealed that calibration-focused models produced 69.86% higher returns. In NBA betting experiments, models optimized for calibration achieved a +34.69% ROI, compared to a -35.17% ROI for accuracy-driven models.
"For the sports betting problem, model calibration is more important than accuracy."
These findings highlight the importance of balance. While machine learning can experience model drift and requires regular retraining, time series models often struggle with non-stationary data due to factors like player fatigue, tactical changes, or injuries. By combining both methods, these weaknesses can be mitigated.
The most effective strategy integrates the strengths of both approaches. For example, WagerProof employs a hybrid method, blending machine learning with time series analysis to deliver well-rounded betting insights. Tools like Edge Finder and WagerBot Chat utilize this combination, reducing overfitting and exposing mispriced odds with greater clarity.
FAQs
How do I know if my model is well-calibrated?
A well-tuned model gives predicted probabilities that align closely with real-world outcomes. To check this, you can use tools like calibration plots, Expected Calibration Error (ECE), and the Brier Score. These metrics are essential for assessing whether your model's probability estimates are trustworthy enough to support sound decisions.
What data do I need for pre-game vs live betting models?
Pre-game models work with static data - things like team statistics, player performance records, historical match outcomes, and external factors such as injuries or weather conditions. These models crunch the numbers before the game even begins, giving you a probability estimate based on everything available at that point.
On the other hand, live betting models are all about real-time updates. They tap into in-game stats like shots on goal, fouls, possession percentages, and even the current score. These models adjust on the fly, reacting to shifts in momentum or unexpected developments during the game. This adaptability can be a game-changer, especially in fast-moving scenarios.
When should I use a hybrid ML + time series approach?
A hybrid machine learning and time series approach works well when aiming to combine the unique strengths of both methods to boost accuracy and profitability in sports betting. This approach captures temporal patterns while utilizing machine learning’s ability to make precise predictions. It's particularly helpful for spotting market inefficiencies or emerging trends. Tools such as WagerProof can enhance this process by identifying value bets and highlighting key outliers in real-time.
Related Blog Posts
Ready to bet smarter?
WagerProof uses real data and advanced analytics to help you make informed betting decisions. Get access to professional-grade predictions for NFL, College Football, and more.
Get Started Free