
Overfitting in Sports Models: Early Stopping Fix
Overfitting ruins sports prediction models by confusing random noise with real patterns. This leads to poor performance during live games, even if the model excelled in backtests. Early stopping is a simple technique to prevent this issue. By monitoring validation error during training, you can stop the process before the model starts memorizing irrelevant data.
Key insights:
- Overfitting: Models perform well on historical data but fail in live scenarios.
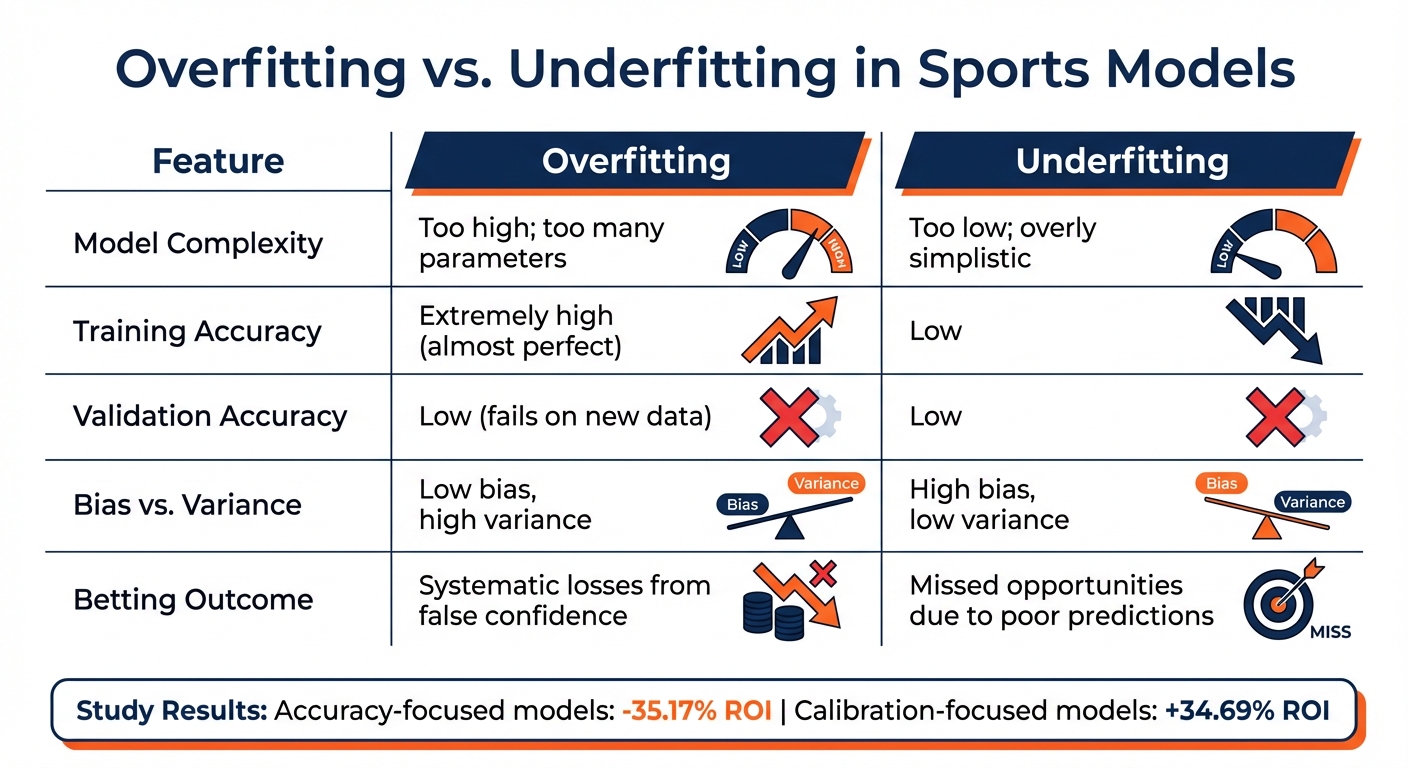
- Impact: Overfitted models can cause financial losses, with one study showing a –35.17% ROI for accuracy-focused models vs. +34.69% for well-calibrated ones.
- Early Stopping: Stops training when validation error rises, ensuring the model focuses on meaningful patterns.
- Best Practices: Use patience (5–20 epochs), set minimum delta (0.001–0.01), and restore the best weights for reliable predictions.
For sports bettors, models that prioritize calibration over raw accuracy deliver better results. Early stopping ensures predictions are reliable and avoids costly mistakes.
Early Stopping in Neural Networks: Preventing Overfitting
How Overfitting Affects Sports Bettors and Predictions
Overfitting vs Underfitting in Sports Prediction Models
Impact on Sports Bettors
Overfitting often tempts sports bettors by showcasing nearly perfect backtesting results, leading them to increase their stakes based on what appears to be a reliable edge. However, when these models face live markets, they frequently fail, unable to identify patterns that hold up in real-world scenarios.
This issue stems from flaws baked into the model from the start. A study conducted in June 2024 by Walsh and Joshi found that models optimized for raw accuracy delivered an average ROI of –35.17%. In contrast, calibration-focused models achieved returns as high as +36.93%. This striking difference underscores how some strategies can grow a bankroll, while others lead to steep losses.
Overfitted models are particularly fragile when the sports landscape shifts. Changes like new rules, roster updates, or fresh coaching strategies expose how poorly these models adapt to evolving conditions. These failures highlight the importance of techniques like early stopping to maintain model reliability - something we’ll delve into further.
Impact on Team Performance Analysis
Overfitting doesn’t just mislead bettors; it also confuses teams and analysts. It can mistake temporary statistical anomalies for genuine skill, leading to expensive recruitment errors or flawed strategic decisions. For example, a model might incorrectly label a player as a star based on a brief hot streak or overestimate a defensive scheme's effectiveness because it has memorized specific past matchups rather than identifying a true advantage.
Overfitting vs. Underfitting
The challenges of overfitting stand in stark contrast to those of underfitting, emphasizing the fine line needed for effective model training. Both issues undermine predictions, but they do so in distinct ways:
| Feature | Overfitting | Underfitting |
|---|---|---|
| Model Complexity | Too high; too many parameters | Too low; overly simplistic |
| Training Accuracy | Extremely high (almost perfect) | Low |
| Validation Accuracy | Low (fails on new data) | Low |
| Bias vs. Variance | Low bias, high variance | High bias, low variance |
| Betting Outcome | Systematic losses from false confidence | Missed opportunities due to poor predictions |
Overfitted models often lure bettors with dazzling backtest results, only to fall apart in live markets - quickly draining their bankrolls. On the other hand, underfitted models lack the complexity needed to capture meaningful patterns, resulting in consistently weak predictions and missed opportunities. Striking the right balance is critical to avoiding these pitfalls.
How Early Stopping Prevents Overfitting
How Early Stopping Works
Early stopping provides an effective way to tackle overfitting by keeping a close eye on how a model performs on a validation set - data specifically set aside to mimic unseen scenarios. After every training cycle (or epoch), the model is tested on this validation set. If the validation error begins to rise while the training error continues to drop, it’s a clear warning sign: the model is starting to memorize noise instead of learning meaningful patterns from the data.
The process relies on a trigger system to determine the right moment to halt training. Training stops as soon as the validation loss increases. However, because sports data often includes random fluctuations - like surprise injuries or unexpected game outcomes - a "patience" parameter is typically added. This parameter waits for several epochs (usually 5 to 10) to confirm that the increase in validation error is consistent. Additionally, a "minimum delta" threshold (commonly set at 0.01) ensures that minor improvements don’t reset the patience counter unnecessarily. Once training stops, the system restores the model to its best version - the one with the lowest validation error.
"Early stopping is a form of regularization used to avoid overfitting when training a model with an iterative method, such as gradient descent." - Wikipedia
By halting training at the right time, early stopping not only prevents overfitting but also boosts the dependability of sports prediction models.
Benefits of Early Stopping for Sports Models
For sports prediction models, early stopping brings some clear advantages. It prevents the model from absorbing random noise from real-time sports data platforms, such as unpredictable upsets or unusual weather events, which are unlikely to repeat. This ensures the model stays focused on learning patterns that generalize well to future games.
Another key benefit is that early stopping acts as an implicit form of regularization. It controls the model’s complexity without altering the loss function itself. Geoffrey Hinton, a leading figure in machine learning, famously described it as a "beautiful free lunch" because of its simplicity and effectiveness. For sports bettors, this matters a lot. A well-calibrated model ensures that when it predicts a 70% chance of a team winning, the outcomes over time align with that probability. By stopping training before overfitting occurs, early stopping helps maintain this crucial balance between predicted probabilities and actual results, ultimately improving both model reliability and betting accuracy.
How to Implement Early Stopping in Sports Models
Preparing Your Data
To make early stopping effective, start by splitting your data correctly. Use three datasets: training data for teaching the model, validation data to track when overfitting begins, and test data to assess the final performance. For sports models, it's crucial to maintain the chronological order of events - train on older games and validate on newer ones. Randomly mixing games from different seasons isn't an option here.
Set aside 10%–30% of the latest data for validation. For instance, if you're creating an NBA prediction model in February 2026, you could train on games from October to December 2025, validate on January 2026 games, and test on February games. This chronological approach mirrors how real-world predictions work, where future games are forecasted based on past performance.
Setting Early Stopping Parameters
Getting the parameters right is key to avoiding premature stopping or excessive training. Here are the most important ones:
- Patience: Defines how many epochs the model waits for improvement before stopping. Sports data, often noisy, typically requires patience values between 5 and 20 epochs.
- Minimum delta: Sets the smallest change that counts as an improvement, usually between 0.001 and 0.01. If this is too high, training stops too soon. If it's too low, the model may waste time learning from noise.
| Parameter | Typical Value | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| monitor | val_loss or val_accuracy |
Metric used to track improvement |
| patience | 5–20 epochs | Number of epochs to wait before stopping |
| min_delta | 0.001–0.01 | Minimum change considered as improvement |
| restore_best_weights | True |
Ensures the best weights from validation are retained |
Always set restore_best_weights to True. This ensures that even if the model continues training for extra epochs, you end up with the version that performed best on the validation set, rather than an overfitted one. For sports betting models, consider focusing on calibration metrics like log loss rather than just accuracy. Accurate probabilities are often more important than simply predicting wins or losses.
Once your parameters are configured, you can move on to selecting the right tools for implementation.
Tools for Early Stopping
Modern machine learning frameworks make early stopping easy to implement. Here's how some popular tools handle it:
- TensorFlow and Keras: These frameworks offer the
EarlyStoppingcallback, which integrates directly into themodel.fit()function. You can specify the metric to monitor, set patience levels, and enable weight restoration with just a few lines of code. - Scikit-Learn: For non-neural network methods often used in sports analytics, like gradient boosting, Scikit-Learn has built-in options such as
early_stopping=Trueandn_iter_no_change. - PyTorch: While it requires a custom class to track validation loss, PyTorch offers more flexibility for handling complex sports models.
These tools are particularly useful for sports models, where the unpredictable nature of game outcomes introduces a lot of noise.
"Early stopping should be used almost universally." - Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville, Authors, Deep Learning (Book)
Studies suggest that using early stopping can speed up convergence by an average of 214% and allow exploration of 167% more configurations within the same time frame.
Case Studies: Early Stopping in Sports Models
Improved Game Predictions
In June 2024, Walsh and Joshi conducted a study exploring early stopping and model calibration in NBA betting. They trained machine learning models using multiple seasons of NBA data and compared two strategies: one focused on accuracy and the other on calibration - assessing how closely predicted probabilities aligned with actual outcomes.
Their findings were striking. Models optimized for calibration achieved an average return on investment (ROI) of +34.69%, while those solely focused on accuracy suffered a –35.17% loss. In the most favorable scenario, calibration-based models delivered a +36.93% ROI, compared to just +5.56% for accuracy-driven models.
"Sports bettors who wish to increase profits should select their predictive model based on calibration rather than accuracy." - Walsh and Joshi
In January 2026, another study introduced an uncertainty-aware forecasting framework for NBA games. Researchers used data spanning 2012 to 2024 to train a recurrent neural network with a strict chronological split - training on games through 2022, validating with 2023 data, and testing on 2024. By employing early stopping through validation sets, this framework achieved superior calibration compared to non-Bayesian models and uncovered opportunities in less-efficient market segments.
These insights highlight the practical advantages of focusing on calibration, a principle embraced by platforms like WagerProof.
WagerProof's Approach to Model Training

WagerProof applies these findings in its statistical models and WagerBot Chat. By incorporating early stopping during training, the platform prioritizes calibration over raw accuracy. This ensures predictions are not only robust but also capable of adapting effectively to new data. This mirrors the University of Bath study, where shifting the focus from accuracy to calibration turned a 35% loss into a 35% gain.
WagerProof also emphasizes transparency. Its tools automatically flag outlier data and highlight potential value bets, while WagerBot Chat connects users directly to live, professional-grade data. This combination helps bettors understand the reasoning behind predictions and make more informed wagering decisions.
Conclusion
Overfitting is a common hurdle in sports prediction models, but early stopping offers a straightforward solution. By halting training when the validation error begins to rise while the training error continues to drop, this method keeps models from memorizing irrelevant historical noise. Instead, it helps them focus on identifying meaningful patterns, leading to predictions that hold up in future scenarios rather than just explaining past outcomes.
A study from the University of Bath highlighted the importance of calibration over raw accuracy, showing how a -35.17% loss was turned into a +34.69% gain by prioritizing well-calibrated probabilities. This is particularly critical for strategies like the Kelly Criterion, where poorly calibrated models, even if seemingly accurate, can cause long-term losses.
To implement early stopping effectively, set patience thresholds to prevent stopping too soon, define minimum delta values to identify genuine improvements, and always restore the model weights from the best validation epoch instead of the final iteration. These finer details distinguish models that succeed in live applications from those that only shine in backtests.
Incorporating early stopping into your models ensures more consistent performance in real-world conditions. Tools like WagerProof and WagerBot Chat apply these principles by identifying outliers and value bets with calibrated predictions, offering clear explanations for each identified edge.
Prioritize models that focus on reliable probabilities rather than perfect historical accuracy. Use early stopping with carefully tuned parameters and rely on platforms that emphasize transparency and calibration. These strategies turn sports betting into a data-driven approach grounded in solid statistical reasoning.
FAQs
How do I know my sports model is overfitting?
A sports model might be overfitting if it shines when analyzing past data but stumbles when forecasting future results. Overfitting occurs when the model fixates on noise or irrelevant details in the historical data, mistaking them for meaningful patterns. This causes the model to struggle with generalizing to new, unseen scenarios.
Key warning signs to watch for:
- Exceptional accuracy when tested on historical data.
- Unreliable or inconsistent performance during live predictions.
This imbalance suggests the model is too tailored to past data, making it less adaptable to real-world situations.
Should I monitor val_loss or a calibration metric for early stopping?
When fine-tuning sports prediction models, it's important to keep an eye on a calibration metric like the Brier Score or Expected Calibration Error (ECE). These metrics are particularly useful because they measure how well the model's predicted probabilities align with actual outcomes. This is crucial for ensuring the model's predictions are not only accurate but also reliable, which is essential in scenarios like sports betting or performance analysis. Using these metrics for early stopping can help prevent overfitting and ensure the model maintains dependable probability estimates.
How do I set patience and min_delta for noisy sports data?
When working with noisy sports data, setting patience and min_delta requires careful consideration of the data's variability.
- Patience determines how many epochs the model should wait for improvement before stopping. For noisy data, a higher patience value, such as 3–5 epochs, is ideal. This helps prevent stopping too early due to minor fluctuations in performance.
- Min_delta specifies the smallest improvement considered meaningful. A small value, like 0.0001, ensures the model focuses on actual trends rather than reacting to random noise in the data.
Balancing these parameters allows the model to adapt effectively without being misled by variability.
Related Blog Posts
Ready to bet smarter?
WagerProof uses real data and advanced analytics to help you make informed betting decisions. Get access to professional-grade predictions for NFL, College Football, and more.
Get Started Free